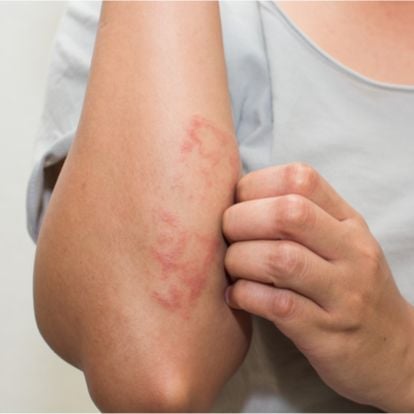
Scabies
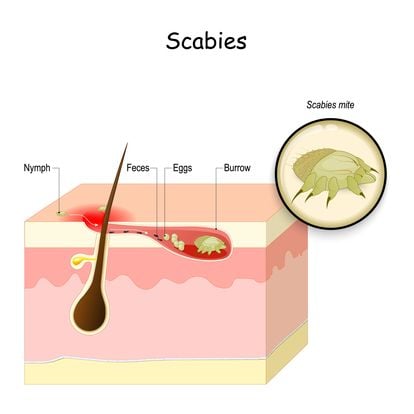
One of the most common skin infections is scabies. Scabies is contagious and can spread through close contact with families, schools, child care, prison, and nursing homes. Due to its infectious nature, it’s important to know the early signs of scabies and what you can do to treat it effectively.
What is Scabies?
Human scabies is from an infestation of the skin caused by the human itch mite called Sarcoptes scabei var. hominins. When placed under the microscope, the mite burrows under the upper layer of the skin and lays eggs.
If somebody is suffering from scabies, it will cause intense itching and a rash that consists of small pimples. Scabies is highly transferable through skin-to-skin contact with somebody suffering from it. Because of this, scabies is more widespread in places that are frequently crowded, which can cause close body contact between people.
For people who have not suffered from scabies before, symptoms can take 4-8 weeks to develop. Even though infected people are not exhibiting symptoms, it is important to know that they can be contagious.
People who previously had scabies will take a shorter time to exhibit symptoms and will usually appear within the first five days of exposure.
Signs and Symptoms of Scabies
The itching caused by scabies is very intense (pruritus) and intensifies more at night. The common areas of the body where the itching occurs are the elbows, wrist, buttocks, waist area, and between fingers.
Another main characteristic of scabies is tiny burrows on the skin, which are caused by female scabies congregating under the upper skin layer.
For severe scabies, vigorous scratching can cause breaking of the skin, which can pave the way for a second bacterial infection such as Impetigo.
Crusted scabies is a more severe form of infection and is most likely seen in high-risk groups such as people with a weakened immune system and those suffering from chronic conditions. For typical scabies cases, the number of mites might be up to 15, but millions of mites can be the source of severe infection for crusted scabies. Because of this, crusted scabies is very contagious and hard to treat.
How is Scabies Diagnosed?
Your doctor or dermatologist will need to examine the affected area to properly diagnose scabies. The symptoms of scabies can be mistaken for other things like dermatitis or eczema, which is why it is essential to get a proper diagnosis to start appropriate treatment.
In looking at the affected area, your doctor will look for burrowing and might even scrape a sample off your skin to put it under the microscope. This microscopic examination can lead to the discovery of mites or their eggs.
Common Treatments for Scabies
The primary treatment for scabies is medications that can eliminate the infection. Your dermatologist might prescribe lotion and creams to alleviate the itching and heal the infection.
The prescribed medication will be applied to your whole body from the neck down and left for at least 8 hours. Some treatments will require a second application.
Because scabies is highly contagious and easily spreadable, the dermatologist will treat people with close contact with the infected person even if they are not exhibiting symptoms.
The usual medication or creams that can be recommended are:
- Crotamiton (Eurex, Croatan)
- Ivermectin (Stromectol)
- Permethrin cream
Consult with your dermatologist to learn which treatment option is right for you.