Atopic Dermatitis
Have you recently experienced dry patches of skin that are red, inflamed, and extremely itchy? You may have atopic dermatitis or eczema and require a consultation from a licensed medical professional or dermatologist. Here’s everything you need to know about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for atopic dermatitis.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
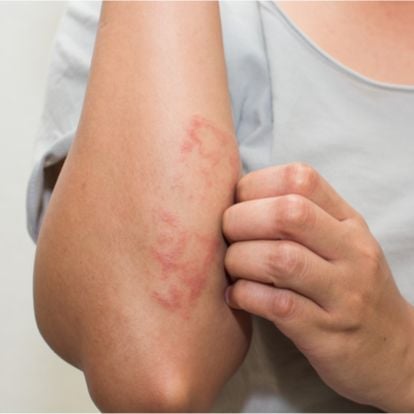
A chronic skin condition, atopic dermatitis results in irritation and inflammation of your skin. It is the most commonly occurring form of eczema. Atopic dermatitis causes redness and itchiness to the affected area of the skin.
Lack of moisture in the top layer of the skin can lead it to dry out and inflammation. As a result of this inflammation, the person is more likely to scratch themselves to satisfy the itch, leading to more damage, redness, swelling, and oozing as the skin gets damaged.
According to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, there is no singular cause for atopic dermatitis. Instead, it can occur as a result of:
- genetics—people with a family history of eczema may be more likely to develop atopic dermatitis themselves
- immune-mediated abnormalities in the skin barrier
- environmental stressors, such as dry weather, hot water, harsh soaps, and fragrances
What Are the Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis?
A chronic inflammatory skin condition, atopic dermatitis first occurs in early childhood and typically resolves by adolescence. However, it is not uncommon for adults to experience atopic dermatitis. In fact, the worldwide prevalence of atopic dermatitis ranges from 2% to 10% in adults in developed countries.
Common symptoms of atopic dermatitis include:
- dry, itchy skin
- rashes on the face, backs of elbows and knees, as well as the hands and feet
- redness
- flaky and/or scaly skin that thickens over time
How is Atopic Dermatitis Treated?
Treatment of atopic dermatitis depends on the symptoms and severity of the disorder. A dermatologist or licensed medical professional can help diagnose your condition and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Prevention of flare-ups and increased healing of the skin barrier are two important and necessary ways to keep atopic dermatitis at bay. It’s not uncommon for your dermatologist to prescribe several therapies to help tackle and manage the symptoms of atopic dermatitis.
Some common forms of treatment for atopic dermatitis include:
- Routine skincare that includes emollients to prevent dry skin
- Avoiding the use of perfumed products on your skin (creams, perfumes, soaps) and clothing
- Topical steroids and non-steroidal agents
- Topical or oral antibiotics, if a skin infection is present
- Medications, including injectables such as biologics that reduce the incidence of inflammation
- Phototherapy, makes use of ultraviolet A or ultraviolet B light waves to treat the condition
What to Expect During a Diagnosis for Atopic Dermatitis
If you’ve never been diagnosed with atopic dermatitis before, you may be wondering what to expect during your appointment with the dermatologist.
A licensed dermatologist will ask you a series of questions regarding your current condition to determine if you’re experiencing any symptoms of eczema. In addition, your provider may ask you questions about your past medical history as well as your family history. Your provider will also perform an exam to evaluate the affected areas of your skin.
Your doctor may suggest tests such as allergy tests before making a diagnosis. Treatment for atopic dermatitis varies from patient to patient and can include the prescription of medications and a new skin care routine.
While there is currently no cure for atopic dermatitis, learning to manage the symptoms can help you live with this chronic skin disorder. Effective atopic dermatitis treatments require an accurate evaluation and prompt care using safe, effective therapies.